TPM Alternatives: Essential Solutions for Computers Without TPM 1.2 or Later
Understand TPM requirements in modern computing
Trust platform module (TPM) has become an essential component in modern computing security. Many current operating systems and security features require TPM version 1.2 or recent to function right. When users encounter systems without this hardware component, they need viable alternatives to maintain security and compatibility with newer software.
What’s a TPM and why’s it important?
A trusted platform module is a specialized chip on the computer’s motherboard that store encryption keys, passwords, and digital certificates. It provides hardware base security functions that protect against firmware attacks and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
TPM 1.2 introduce key improvements in security protocols, while TPM 2.0 bring additional enhancements for modern security needs. These modules have become progressively important as operate systems like Windows 11 list TPM 2.0 as a system requirement.
Hardware solutions for computers without TPM
TPM add on modules
For desktop computers without an integrate TPM, users can insert a compatible TPM module into their motherboard. These modules typically connect to a dedicated TPM header on compatible motherboards. When purchase a TPM add on module, users must ensure:
- The module match their motherboard’s specifications
- The motherboard have a TPM header connection
- The module meet the minimum version requirements (1.2 or 2.0 )
Installation involve cautiously insert the module into the designated header on the motherboard. After physical installation, users must enable the TPM in bios / UEFI settings.
TPM compatible security devices
External security devices can provide TPM like functionality for systems without build in TPM support. These include:
- Hardware security keys (like yYubiKeyor titan security key )
- USB security dongles with encryption capabilities
- Smart card readers with compatible security cards
While these devices don’t replace all TPM functions, they can provide authentication and some encryption capabilities that satisfy specific security requirements.
Software alternatives to TPM
Virtual TPM solutions
For systems that can not accommodate physical TPM modules, virtual TPM (vTPM))ffer a software base alternative. Virtual tpmTPMulate tpmTPMnctionality through software, provide many of the same security benefits. Implementation options include:
- Hypervisor base TPM for virtual machines
- Firmware TPM solutions provide by some manufacturers
- Third party TPM software solutions
While not adenine secure as hardware base TPM, TPM can satisfy many security requirements and enable compatibility with systems require tTPM
Registry modifications and bypass methods
For Windows systems, registry modifications can bypass TPM requirements for specific features or installations. These methods include:
- Appraiser bypass Regg files foWindowsws 11 installation
- Group policy modifications to override TPM checks
- Installation scripts that skip hardware checks
It’s important to note that these methods circumvent security measures design to protect your system. Users should cautiously consider the security implications before implement these workarounds.
Specific solutions for Windows 11 compatibility
Windows 11 installation workarounds
Windows 11 formally requiresTPMm 2.0, but users with older hardware can insert specific bypass commands during installation:
- Create a Windows 11 installation media
- During installation, press shift+f10 to open command prompt
- Type” rreedit”” open registry editor
- Navigate to hey_local_machinesystemsetup
- Create a new key call” llab confi”
- Inside lab config,created wordd values:
- Bypasstpmcheck (value: 1 )
- Bypasssecurebootcheck (value: 1 )
- Bypassramcheck (value: 1 )
- Close registry editor and continue installation
Instead, users can use the Rufus tool to create installation media with these bypasses pre-configure.
BitLocker alternatives
BitLocker, windows’ build in disk encryption, typically require TPM. For systems without TPM, users can:
- Configure BitLocker to work without TPM through group policy
- Use alternative encryption software like Veracruz or ddescriptor
- Implement file level encryption alternatively of full disk encryption
These alternatives provide encryption capabilities without require TPM hardware, though they may require additional authentication steps during system startup.
Bios / UEFI configuration options
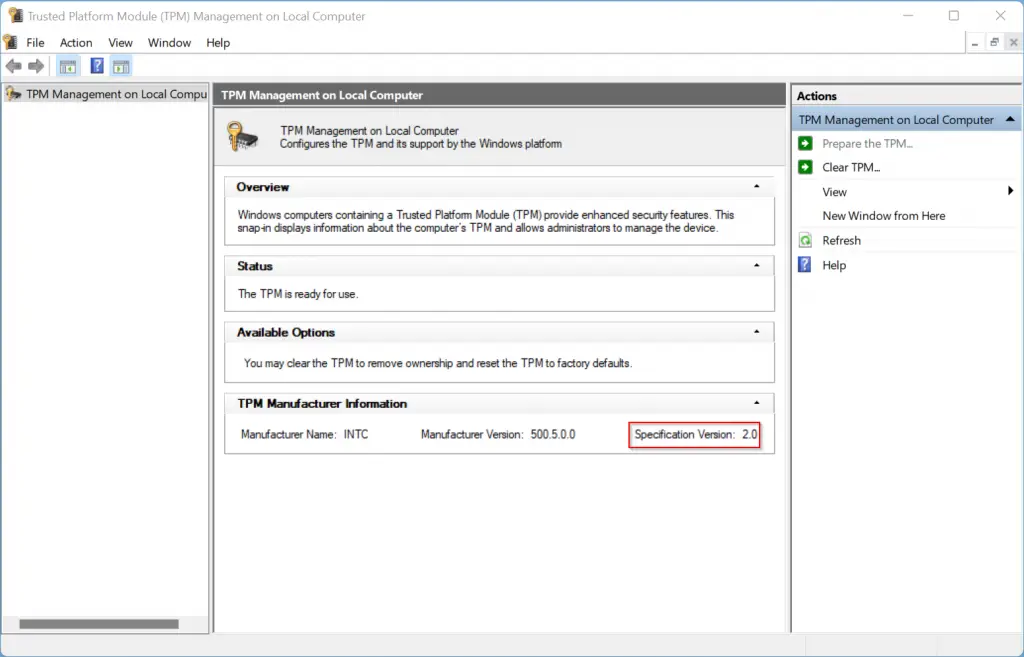
Enabling firmware TPM
Many modern systems include firmware base TPM implementations that can be enabled in bios /UEFIi settings:
- Restart the computer and enter bios / UEFI (typically by press f2, dDel or f10 during startup )
- Navigate to the security, advanced, or trusted computing sections
-
Look for options label” fTPM”” amdAMDstems ),) p” “PTT” el platform trust technology ), or) firm” e tpm ”
TPM” - Enable the appropriate option
- Save changes and exit
This solution work for many systems manufacture within the last 5 7 years, evening if they don’t have a dedicated TPM chip.
Security settings adjustment
For systems that can not support any form of TPM, adjust other security settings can help mitigate risks:
- Enable secure boot if available
- Configure strong bios / UEFI passwords
- Disable legacy boot options
- Enable drive encryption through alternative means
These settings enhance security level without TPM functionality.
Enterprise solutions for TPM requirements
Network security alternatives
In enterprise environments, network base security measures can compensate for miss TPM functionality:
- Network access control (nNAC)systems to verify device security status
- VPN solutions with strong authentication requirements
- Zero trust security architecture that verify each access request
- Remote attestation services that validate device integrity
These solutions shift security verification from the local TPM to network infrastructure, maintain protection for sensitive resources.
Managed security services
Organizations can implement manage security services that provide TPM like functionality through alternative means:
- Cloud base key management services
- Centralized authentication systems
- Endpoint protection platforms with encryption capabilities
- Mobile device management (mMDM)solutions with security enforcement
These services provide centralized control over security policies without require TPM hardware on each device.
Considerations when bypassing TPM requirements
Security implications
Before implement TPM alternatives or bypasses, users should understand the security implications:
- Reduced protection against certain types of attacks
- Potential vulnerability to boot level malware
- Less secure key storage for encryption
- Possible exposure of sensitive authentication data
These risks should be weighed against the benefits of use newer operating systems or security features.
Compatibility and support limitations
Systems run without require TPM may experience:
- Limited or no official support from operate system vendors
- Inability to install future security updates
- Incompatibility with certain applications or features
- Performance issues with security dependent functions
Users should consider these limitations when decide whether to bypass TPM requirements or upgrade their hardware.
Long term solutions and hardware upgrades
Plan for hardware replacement
While workarounds can extend the usability of older systems, plan for hardware upgrades provide a more sustainable solution:
- Budget for systems with integrated TPM 2.0
- Consider motherboard upgrades for desktop systems
- Evaluate the cost benefit of new hardware versus security risks
- Implement phase replacement strategies for enterprise environments
Modern systems with integrated TPM provide the virtually secure and compatible platform for current operating systems.
Transitional security strategies
During the transition to TPM equip hardware, users can implement additional security measures:
- Multifactor authentication for all sensitive accounts
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
- Network segmentation to isolate non TPM systems
- Enhanced monitoring for suspicious activities
These strategies help maintain security during the transition period.
Conclusion
When face with computers lack TPM 1.2 or recent, users have several options to maintain compatibility with modern security requirements. Hardware solutions like add on TPM modules provide the virtually direct approach, while software alternatives offer flexibility for systems that can not accept physical upgrades.

Source: toolspond.com
For temporary needs, registry modifications and installation bypasses can enable compatibility with TPM require software. Yet, users should consider the security implications and plan for hardware upgrades when practical.
By understand the available options and their trade-offs, users can make informed decisions about how to address TPM requirements while maintain system security and functionality. Whether through hardware additions, software alternatives, or strategic workarounds, solutions exist for virtually every system configuration.

Source: jnv.autoprin.com