Traditional Education: Understanding Conventional Learning Systems and Their Core Principles

Understand traditional education
Traditional education represent the conventional approach to learn that has dominated educational systems worldwide for centuries. This time test method centers around structured classroom environments where teachers serve as primary knowledge sources, deliver curriculum through direct instruction to groups of students organize by age and grade level.
The foundation of traditional education rests on establish pedagogical principles that emphasize systematic knowledge transfer, standardized curricula, and formal assessment methods. Students typically progress through predetermine educational stages, follow a linear path from elementary through secondary education, with clear define learn objectives and measurable outcomes.
Core characteristics of traditional learning systems
Traditional education operate through several defining features that distinguish it from alternative educational approaches. The teacher center model place educators at the center of the learning process, with instructors serve as authoritative sources of information who guide students through structured lessons and activities.
Classroom base instruction form the primary delivery method, where students gather in physical spaces design for group learning. These environments typically feature rows of desks face a blackboard or whiteboard, create a formal atmosphere conducive to focus attention and note-taking.

Source: usheredu.com
Standardized curricula ensure consistency across institutions, with predetermined learn objectives, textbooks, and materials that align with educational standards. This systematic approach guarantee that students receive comprehensive coverage of essential subjects disregarding of their specific school or location.
Age base grouping organize students into grades or classes base mainly on chronological age sooner than individual learn pace or ability levels. This structure facilitate administrative efficiency and enable teachers to plan lessons appropriate for specific developmental stages.
Teach methods and instructional approaches
Traditional education employ time test instructional methods that have proved effective across diverse student populations. Direct instruction serve as the primary teaching strategy, where educators present information through lectures, demonstrations, and guide practice sessions.
The lecture format allow teachers to expeditiously convey large amounts of information to entire classes simultaneously. Students listen, take notes, and ask questions during designate times, create an orderly learn environment that maximize content coverage within limited timeframes.
Textbook base learning provide structured knowledge sources that align with curriculum standards. These cautiously curate materials present information in logical sequences, offer consistent quality and comprehensive coverage of subject across different educational institutions.
Homework assignments extend learn beyond classroom hours, reinforce concepts through independent practice and application. This approach help students develop self-discipline, time management skills, and deeper understanding through repetition and reflection.
Regular testing and examinations assess student progress and mastery of material. These formal evaluation methods provide measurable data about learn outcomes to prepare students for standardized assessments and future academic challenges.
Subject organization and curriculum structure
Traditional education organize learn into distinct subject areas, each with specialized content, methodologies, and assessment criteria. Core subjects typically include mathematics, language arts, science, and social studies, form the foundation of comprehensive education.
Mathematics instruction follow sequential progressions from basic arithmetic through advanced topics like algebra, geometry, and calculus. This systematic approach builds upon antecedently learn concepts, ensure students develop strong computational skills and logical reasoning abilities.
Language arts education encompass reading, writing, speak, and listening skills through literature study, grammar instruction, and composition practice. Students engage with classic and contemporary texts while develop communication abilities essential for academic and professional success.
Science education introduce students to scientific methods, natural phenomena, and technological applications through biology, chemistry, physics, and earth sciences. Laboratory experiments and demonstrations provide hands-on experiences that complement theoretical knowledge.
Social studies instruction cover history, geography, civics, and cultural studies, help students understand human societies, governmental systems, and global interconnections. This broad field develop critical thinking skills and cultural awareness necessary for informed citizenship.
Assessment and evaluation methods
Traditional education rely on formal assessment methods that measure student achievement through standardized criteria and comparative rankings. These evaluation systems provide quantitative data about learn progress while maintain consistency across different educational settings.
Write examinations test knowledge retention, comprehension, and application through multiple choice questions, short answers, and essay responses. These assessments allow teachers to evaluate large numbers of students expeditiously while maintain objective scoring standards.
Grade base reporting systems translate assessment results into letter grades or numerical scores that indicate performance levels relative to established standards. This approach facilitate communication between educators, students, and parents while provide clear indicators of academic progress.
Standardized testing ensure consistency across institutions and regions, enable comparisons between different schools, districts, and educational systems. These assessments help identify areas need improvement while maintain accountability for educational outcomes.
Report cards and transcripts document student achievements over time, create permanent records that support advancement decisions and future educational opportunities. These formal documents serve as credentials for college admissions, scholarship applications, and employment opportunities.
Benefits and advantages
Traditional education offer numerous advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption and continued relevance in educational systems universal. The structured environment provide clear expectations, consistent routines, and organize learning experiences that benefit many students.
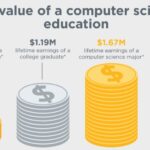
Proven effectiveness demonstrate the success of traditional methods in produce educate graduates who contribute meaningfully to society. Generations of professionals, leaders, and innovators have emerged from traditional educational systems, validate the approach’s fundamental soundness.

Source: collidu.com
Systematic knowledge transfer ensure comprehensive coverage of essential subjects and skills. The organized curriculum guarantee that students receive intimately rounded educations that prepare them for higher learning and professional responsibilities.
Social development opportunities arise course through classroom interactions, group projects, and extracurricular activities. Students learn cooperation, communication, and leadership skills while build friendships and professional networks that benefit them throughout their lives.
Preparation for standardized assessments help students develop test take skills and academic discipline necessary for college admissions and professional certifications. This preparation provide practical advantages in competitive educational and career environments.
Challenges and limitations
Despite its many strengths, traditional education face criticism regard its ability to address diverse learning needs and adapt to change societal demands. Several limitations have prompt discussions about educational reform and alternative approaches.
One size fits all approaches may not accommodate different learning styles, paces, or interests efficaciously. Some students thrive in traditional environments while others struggle with rigid structures and standardized expectations that don’t align with their individual needs.
Limited individualization can prevent students from pursue personal interests or develop unique talents that fall outside standard curricula. The emphasis on conformity and standardization may discourage creativity and independent thinking in some learners.
Passive learning models position students as recipients preferably than active participants in the educational process. This approach may not full engage students or develop the critical thinking and problem solve skills progressively value in modern workplaces.
Technology integration challenges arise as traditional systems adapt to digital tools and online resources. Many institutions struggle to incorporate new technologies efficaciously while maintain the structured approaches that define traditional education.
Traditional education in the modern context
Traditional education continue to evolve to address contemporary challenges while preserve its core strengths. Many institutions blend traditional methods with innovative approaches, create hybrid systems that combine prove techniques with modern educational insights.
Technology integration enhance traditional instruction through interactive whiteboards, educational software, and online resources that supplement textbook base learning. These tools maintain structured approaches while expand access to information and engage students through multimedia presentations.
Differentiate instruction within traditional frameworks allow teachers to modify their approaches for diverse learners while maintain standardized curricula and assessment methods. This flexibility help address individual needs without abandon prove educational structures.
Professional development programs help traditional educators incorporate new teaching strategies, assessment methods, and technological tools into their practice. This ongoing training ensure that traditional systems remain current and effective in change educational landscapes.
Parent and community involvement strengthen traditional education through volunteer programs, fundraising efforts, and advocacy initiatives that support schools and teachers. These partnerships create supportive environments that enhance student success within traditional educational frameworks.
Compare traditional and alternative approaches
Understand traditional education require examine how it differs from alternative educational philosophies and methods that have gain popularity in recent decades. These comparisons highlight the unique characteristics and benefits of conventional approaches.
Montessori education emphasize child direct learning and mixed age classrooms, contrast with traditional age base grouping and teacher lead instruction. While Montessori methods promote independence and self motivation, traditional approaches provide more structured guidance and systematic skill development.
Waldorf education focus on artistic integration and delay academic instruction, differ from traditional emphasis on early literacy and standardized curricula. Traditional methods prioritize measurable academic achievement while Waldorf approaches emphasize holistic development and creativity.
Homeschooling allow personalized instruction and flexible scheduling that traditional schools can not match. Notwithstanding, traditional education provide social interactions, specialized facilities, and professional instruction that home environments may lack.
Online learning offer convenience and accessibility but may not provide the structured environment and direct teacher interaction that characterize traditional education. Many students benefit from the routine, accountability, and social aspects of conventional classroom settings.
The future of traditional education
Traditional education continues to adapt to meet evolve societal needs while maintain its fundamental principles and prove methodologies. The future potential hold continued integration of new technologies, teaching methods, and assessment approaches within traditional frameworks.
Blend learning models combine traditional classroom instruction with online components, create flexible systems that preserve the benefits of both approaches. These hybrid methods maintain structured learning environments to incorporate digital tools and resources.
Competency base progression may supplement traditional age base grouping, allow students to advance base on mastery sooner than time spend in courses. This modification preserve systematic curricula while accommodate individual learn paces.
Enhanced teacher training programs prepare educators to use new technologies and teaching methods within traditional settings. This professional development ensure that conventional systems remain effective and relevant in change educational landscapes.
Continue research into learn sciences inform improvements to traditional methods without abandon their core principles. Evidence base modifications help traditional education evolve while maintain its proven effectiveness and widespread applicability.
Traditional education remain a cornerstone of educational systems worldwide, provide structure, comprehensive learning experiences that prepare students for academic and professional success. While alternative approaches offer valuable innovations, traditional methods ccontinue to demonstratetheir effectiveness in develop knowledgeable, skilled, and responsible citizens who contribute meaningfully to society.